- AI Weekly Wrap-Up
- Posts
- New Post 10-29-2025
New Post 10-29-2025
Top Story
Nvidia reveals ambitious roadmap
This week, premiere AI chipmaker Nvidia brought its GPU Technology Conference to Washington, DC, and its rock-star CEO Jensen Huang laid out a series of futuristic goals for the company, for AI, and for the world.
Jensen announced:
Nvidia’s advanced Blackwell AI chips are now being manufactured in the US, at TSMC’s multi-billion-dollar chip fabrication facility in Phoenix, Arizona.
Nvidia will partner with Oracle to build 7 massive AI supercomputers for US national labs, beginning with 2 for the Department of Energy’s Argonne lab.
The company is moving aggressively to link its GPUs with quantum computers, starting with 17 US quantum computing companies.
Partnering with Nokia for AI-native 6G cellular service: Nvidia will invest $1 billion for a stake in the once-dominant cellphone maker, similar to its deal with Intel, another former star that has fallen on hard times. Nvidia wants to ensure that 6th-generation cellular service is not all based on technology from the Chinese, who are reportedly far ahead.
Autonomous robo-taxis with Uber: Uber promises to launch a fleet of 100,000 robotaxis starting in 2027, all guided by Nvidia’s AI chips and its “DriveOS” operating system.
Robots, robots, robots: Nvidia proposes to reindustrialize America with automated factories full of industrial robots.
Re-entering the Chinese market: The tariff war and US export controls have dropped Nvidia’s market share in China from 95% to 0%, and China is ramping up its own chip production. Jensen vows to re-enter China in a significant way in the coming years. Pro tip: never bet against a man who started out as a bus boy at Denny’s and became the CEO of the most valuable company in the world.
Nvidia brought this particular road show to Washington for a reason - to influence US policymakers, and in particular the President. Jensen has learned how to work with Trump, and many of his initiatives are packaged in terms that appeal to the President’s America First priorities.

CEO Jensen Huang lays out an ambitious future for Nvidia and AI.
Clash of the Titans
Amazon plans to shave 160,000 US jobs by 2027, 600,000 by 2033
Amazon internal documents obtained by the New York Times reveal that the dominant online retailer plans to greatly increase the use of AI, automation, and robotics in order to eliminate the need for up to 600,000 US workers between now and 2033. Most of the savings are projected to come from avoiding hiring more workers as the company grows - it expects to double its volume of sales in that period. Some 160,000 job eliminations are expected in the next 2 years, as Amazon converts 75% of operations at its fulfillment warehouses to robots. Amazon currently has 1.5 million employees, making it the second largest employer in the US (Walmart has 1.6 million.) Amazon also uses approximately 1 million robots. In the next several years expect that ratio to reverse.

Amazon robots come in all shapes and sizes, including these floor gliders that haul racks of items.
AI workers embrace 100-hour work weeks to win the AI arms race
In this new Age of AI, warehouse workers may be on the chopping block (see story above), but employees in AI companies are working 100-hour weeks in a mad race to be the first to achieve AI superintelligence. There is a pervasive feeling that this is a pivotal moment in history and that the stakes are enormous: for starters, the possibility of unimaginable wealth; the solutions to pressing problems such as poverty, disease, and climate change; and even which nations will dominate the future. At the same time, there is a sense that the breakthroughs may be very close, and whoever wins the race may alter the course of history. For technology companies, AI development is a global Manhattan Project, where some of the smartest people in the world pour everything they have in pursuit of a singular goal. And where coming in second may be equivalent to finishing last.

Employees in AI companies are toiling long hours in pursuit of superintelligence.
OpenAI finally transitions to a for-profit organization
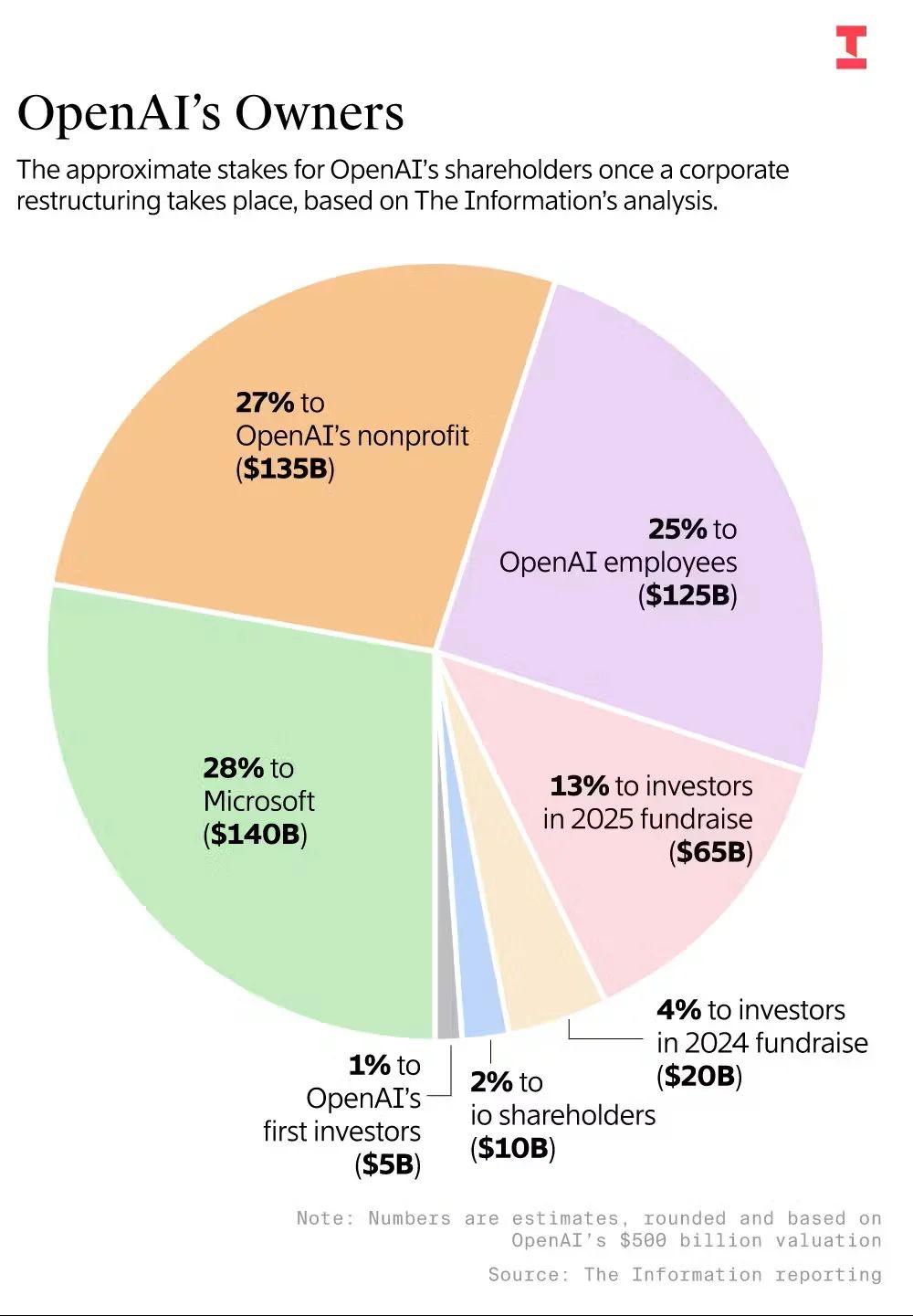
OpenAI started out in 2015 as a nonprofit research lab, with the idealistic goal of making sure that AI was available to everyone, not just governments and tech billionaires. Things obviously changed once their success with ChatGPT demonstrated that ungodly amounts of money could be made by hawking AI to the masses. Their nonprofit structure and profitable mission has caused the company no end of complications as it grew into the most valuable private company on the planet (currently worth some $500 billion.)
Yesterday, after fending off a lawsuit by Elon Musk, renegotiating their partnership with Microsoft, and satisfying the demands of the Attorneys General of California and Delaware, OpenAI completed a restructuring and recapitalization process that converted it to a public benefit corporation. This is a special type of corporation that is legally required to strive for a balance between the interests of shareholders and its public-benefit mission.
The nonprofit organization will own a 27% stake in the new company (currently worth $135 billion, making it the largest charitable foundation in the world), and will have special voting rights. Microsoft will also have approximately 28% of the new entity. The remaining 45% is owned by a Who’s Who roster of VCs and top tech investors, as well as employees.
Fun News
Google’s quantum computer outpaces world’s best supercomputer
Google has announced that its Willow quantum computing device has completed a complex real-world computing task 13,000 times faster than the world’s most powerful supercomputer. They claim that this is the first-ever verifiable quantum advantage for a real-world physics problem, not just toy problems devised for research. The calculation predicts how fast a quantum signal will travel across a quantum chip. The writeup of the experiment has been published in the prestigious scientific journal Nature. This 13,000-fold speedup is one of the few precise measurements of quantum computing’s promise. And while admittedly impressive, this level of acceleration is far below the power needed to break modern cryptographic methods, such as those that underlie financial transactions and encrypted email. Doomsayers have predicted for years that quantum computing means the instant end of all security and privacy online. Well, that seems to be an exaggeration, at least for now. But a 13,000-fold speedup of computing could give everyone in the world access to 1000 times more AI.

Google CEO Sundar Pichai stands by his company’s new quantum computer.
Amazon is developing smart glasses for drivers
In its relentless pursuit of efficiency , Amazon is now developing AI-powered smart glasses that assist drivers at every step of package delivery. The glasses feed information to the driver in an overlay over whatever they are looking at (see illustration below.) Once the driver parks the vehicle at a delivery location, the glasses automatically activate. They help the driver locate the correct packages in the vehicle, then give turn-by-turn walking directions to the correct delivery address. Once there, the glasses assist with taking a delivery confirmation photo, and navigation back to the vehicle. Amazon’s concept of real-time smart assistance with AI glasses seems like a peek into the future of many jobs that require handling materials in real-world environments.

A view through a prototype of Amazon’s smart glasses for delivery drivers.
Data centers need so much power, they are using old aircraft engines
AI data centers are notorious energy guzzlers. The pace of data center construction is so far outpacing the building of the electrical infrastructure to support them, that in some areas data center operators are purchasing refurbished jet airplane engines, bolting them to a trailer, and using them to power electrical generators. It’s a quick but noisy (and environmentally suboptimal) solution for the energy crunch.

Technician refurbishing a used jet aircraft engine to power a datacenter.
China’s DeepSeek dominates AI investing tournament
AI research lab “nof1” has launched a financial trading tournament between several top AI models. Each model was allocated $10,000 in real money, given access to a cryptocurrency trading exchange, and instructed to maximize returns over the course of a two-week “season.” The results of the models’ trades are tracked online in real time (see link below.) At this point, DeepSeek and Qwen, both open-source models from China, are far ahead of the rest of the pack. Closed-source Western models ChatGPT and Gemini are currently near the bottom in performance, with Claude in the middle.

Alpha Arena pits AI models against each other in trading cryptocurrencies.
Robots
China’s 16,000-drone lightshow breaks world records
The city of Liuyang, China mounted a record-breaking drone light show to celebrate China’s autumn festival. 15,947 drones carrying 7,496 fireworks were launched, and seamlessly morphed into shapes such as a DNA double helix, a blooming flower, butterflies, and a tree. Feather-shaped fireworks burst forth from the branches of the tree. The display broke two Guinness World Records: one for most drones simultaneously launched and controlled by a single computer, and one for most fireworks carried by a drone swarm.

A tree of drones drops fireworks leaves in Liuyang, China light show.
Silicon Valley startup designs AI-powered fighter-jet “wingman”
Defense-tech startup Shield has designed a jet-powered AI drone that will act as a “wingman” to human-piloted fighter jets. The AI drone, named X-Bat, looks like a shrunken B-2 bomber. It is designed to fly autonomously in formation with piloted fighter jets, in order to extend sensor range, enhance threat detection, and improve rapid response to hostile aircraft.

The Shield X-Bat AI drone will help defend fighter jets.
AI in Medicine
Healthcare is adopting AI faster than most other industries in the US
Often considered a technological laggard, the healthcare industry is a leader in adopting AI. A recent survey by VC firm Menlo Ventures indicates that 22% of healthcare organizations in the US have adopted one or more AI tools, as compared to only 9% of US businesses in general. Much of this is driven by the rapid adoption of AI Scribe tools for documenting clinical encounters, which relieves a major pain point for clinicians, but also has obvious applications for coding and billing. Now that the first wave of AI adoption for clinical documentation has begun to solidify, healthcare organizations are looking to use AI for operational efficiencies and cost saving, which may reduce administrative headcount.
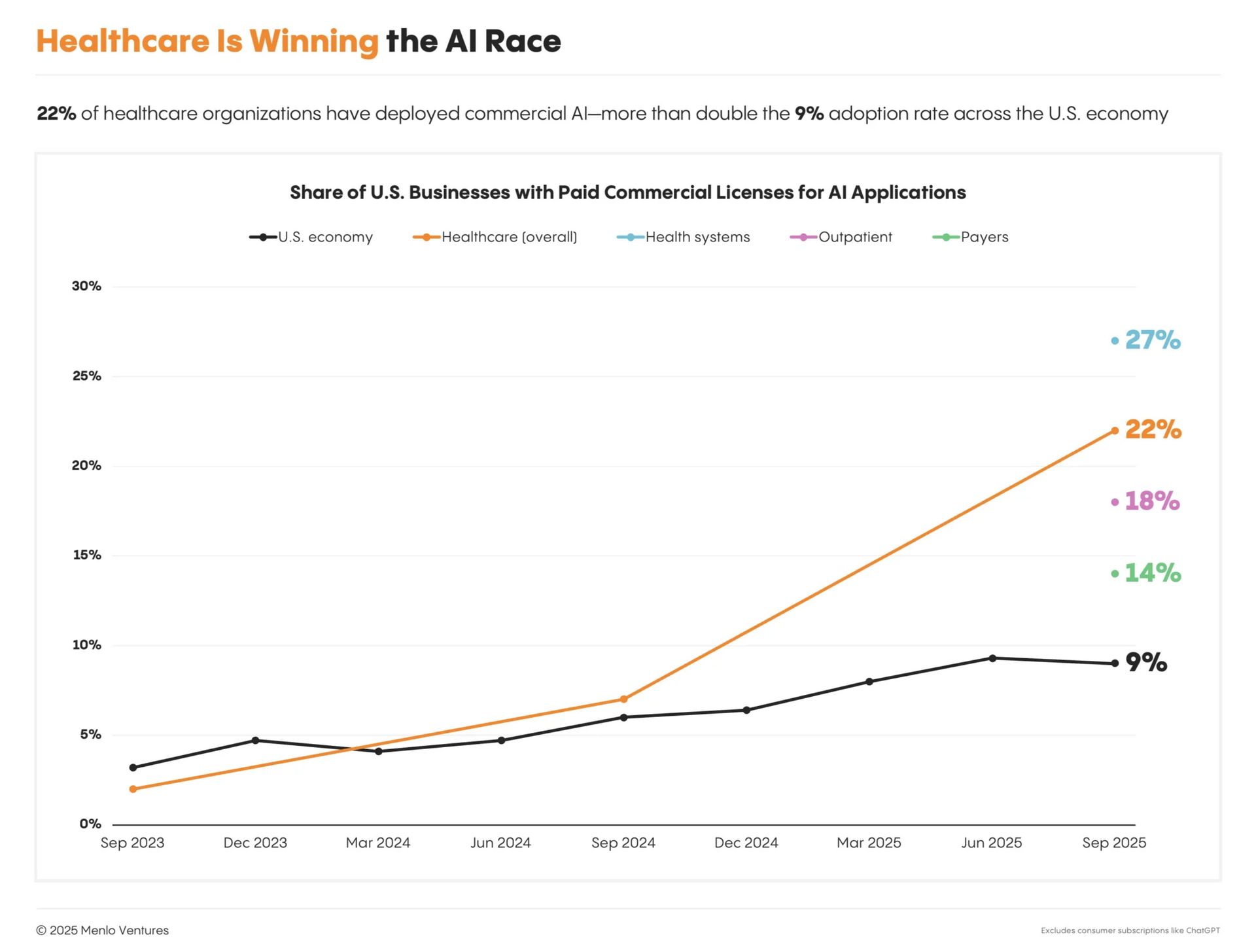
Healthcare organizations are adopting AI at a rate more than twice that of US businesses in general.
Researchers reverse brain aging in mice with human stem cells
Cedars-Sinai researchers have demonstrated a method to reverse brain aging and cognitive decline in mice, using bioengineered human stem cells. They first used human stem cells to produce new, “young” immune cells known as mononuclear phagocytes. These are cells which normally circulate in the bloodstream to clear harmful substances, but they tend to lose efficacy as the organism ages. When mice with cognitive decline were infused with these “youthful” immune cells, memory and cognition improved, and the brain structures involved in memory showed improvement as well. This study uses similar bioengineering techniques as a recent Chinese paper on reversing multiple aging factors in macaque monkeys (see link below.)

Bioengineered mononuclear phagocytes reversed cognitive decline in mice.
That's a wrap! More news next week.