- AI Weekly Wrap-Up
- Posts
- New Post 5-7-2025
New Post 5-7-2025
Top Story
Visa wants to give AI Agents your credit card
Credit card giant Visa has announced that it is allying with AI companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google, to create a framework in which AI “Agents” are given the ability to use your credit card to make purchases without your explicit confirmation. Mastercard and PayPal are working on similar projects. The utopian dream here is of AI Agents as personal assistants, doing the tedious work of booking flights, hotels, restaurants and more, armed with knowledge of your preferences, constraints, and budget. Who wouldn’t want such a smart personal assistant? (Moi, for one, would love one.) The potential dystopian nightmare of such a framework is that such an Agent might not really be your Agent, but a superpowered adbot that would buy things you don’t need without checking with you, while serving up your intimate details to the AI company that makes the underlying AI model, so they can get ever better at tempting you. This is a development that bears watching closely.

Soon AI will be able to spend your money for you.
Clash of the Titans
OpenAI drops for-profit conversion, troubles still linger
OpenAI has finally thrown in the towel, concluding that regulators are unlikely to approve its proposed conversion from a nonprofit organization to a for-profit corporation. It now proposes to leave its nonprofit Board in place, and to convert its profit-making LLC subsidiary into a “Public Benefit Corporation”, a type of corporate structure that requires the company to make a positive contribution to society over and above any profits earned. This surrender doesn’t end OpenAI’s troubles, because investors who have up to now bid up shares of OpenAI to the stratosphere may have less appetite for the new structure, which could limit their returns. In addition, Microsoft, which has to date invested over $13 billion into the company, is said to be withholding approval of the new plan, and is negotiating terms. And finally, Elon Musk’s lawsuit against the company’s restructuring away from its nonprofit origin is still ongoing, even after events have given Elon most of what he says he wants. Of note, Elon’s Grok AI model is a direct competitor of OpenAI’s ChatGPT, and anything that slows OpenAI down in the AI race helps put money in Elon’s pocket.

OpenAI CEO Sam Altman puts on a happy face after giving up on his plan for restructuring.
Mark Zuckerberg wants Facebook to create your AI friend
In a recent podcast with techbro interviewer Dwarkesh Patel, Meta/Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg indicated that the company is working on AI chatbots that will interact with humans as a friend and confidante. He proposes this development as a possible solution to today’s “loneliness epidemic.” Now, Zuck’s fondness for digitally mediated friendship is well-known, from the original Facebook, to his ill-starred effort to get everyone to participate in a simulated online world he called the “metaverse”. (He even changed the name of his company to Meta.) But Z-boy is not the only AI aficionado hyping the AI-as-friend narrative. Microsoft’s head of AI, Mustafa Suleyman, has enthused about converting the company’s apps into a friendly and helpful companion. A recent effort in this direction had to be withdrawn, when users complained that it was trying to be their friend when they just needed a tool. The idea of making their product your friend is enticing to AI companies, because humans are generally more loyal to friends than to products.

Meta/Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg socializing with actual people in real life.
Argentina plans small nuclear power plants to attract data centers
What’s a small country to do to get investments to boost its economy? If the country is Argentina, the answer seems to be to hop onto several hot trends at once - the AI frenzy, the consequent need for data centers, the associated necessity of guaranteeing adequate electricity for all those power-hungry servers, and the latest fad in nuclear power plants, small modular reactors. Argentina’s President Javier Milei is backing an ambitious plan to make his country a nuclear power hub, rolling out scads of small nuclear reactors to entice AI companies to build data centers in this land of tango, empanadas and soccer fanatics. Bold. Creative. Probably unrealistic, since there is not yet a single commercial small modular reactor in the world. SMR’s have many theoretical advantages, and prototypes have been tested, but nobody knows how to make them commercially.

Argentina’s President Javier Milei has a bold vision of nuclear-powered data centers.
Fun News
“Vibe coding” race heats up further
It now seems clear that one of the first industries to be transformed by AI will be software development. In recent months, the ability of AI models to write working computer code has skyrocketed, to the point where the CFO of OpenAI claims that one of their models is the best coder on the planet, better than all humans. Writing computer code by prompting an AI model has acquired the catchy name of “vibe coding.” Multiple startups are chasing the vibe coding wave, and the larger AI companies are going all-out to ratchet up their vibe code offerings. OpenAI tried to buy developer favorite Cursor, but that startup decided to go it alone and raised $900 million at a valuation of $9 billion. So OpenAI has just agreed to buy a Cursor competitor, Windsurf, for $3 billion. Anthropic has recently signed a deal with Apple to build a joint vibe coding tool. And just yesterday, Google announced an upgrade to its flagship Gemini 2.5 Pro model, which is turning heads for its ability to quickly develop interactive web applications.

Using AI to write computer software is all the rage.
Reddit tightens verification in wake of unethical research on members
Online forum Reddit has announced that it is tightening its authentication and verification systems, in the wake of a recent scandal, in which researchers from the University of Zurich ran a covert, unauthorized, and highly `unethical study of AI persuasiveness that duped forum members with untrue and misleading information. The study was only discovered when the researchers published their results in an online scientific journal. The researchers violated Reddit terms of service by having AI bots pose as actual humans. They then used the bots to try to change participants’ minds on political topics, using false and misleading information. The results were that the AI bots were able to get users to change their minds at a rate far exceeding the best results for human persuasiveness from other studies. Now Reddit is threatening legal action against the researchers, and is simultaneously investing in verification systems that are designed to weed out bots. Verification is a tricky issue for Reddit, whose free-wheeling and often highly-opinionated forums depend on users being able to stay anonymous. Nonetheless, this alarming breach has forced them to consider drastic measures.

Reddit is being forced to tighten verification of users in wake of research scandal.
LLM impact on website traffic - searches are down, authenticity is up
How are chatbots affecting web traffic to various sites? One tech blogger crunched the publicly available numbers and found - no surprise - that sites where users go to find answers (such as WebMD) or to comparative shop (like CNET) were down. Why scroll through a site when you can just ask ChatGPT? Less expected, some sites are thriving in the age of chatbots, chiefly those which include authentic opinions from individuals (like Reddit or Substack.) It appears that, at least for now, access to AI makes humans value authentic humanness more.
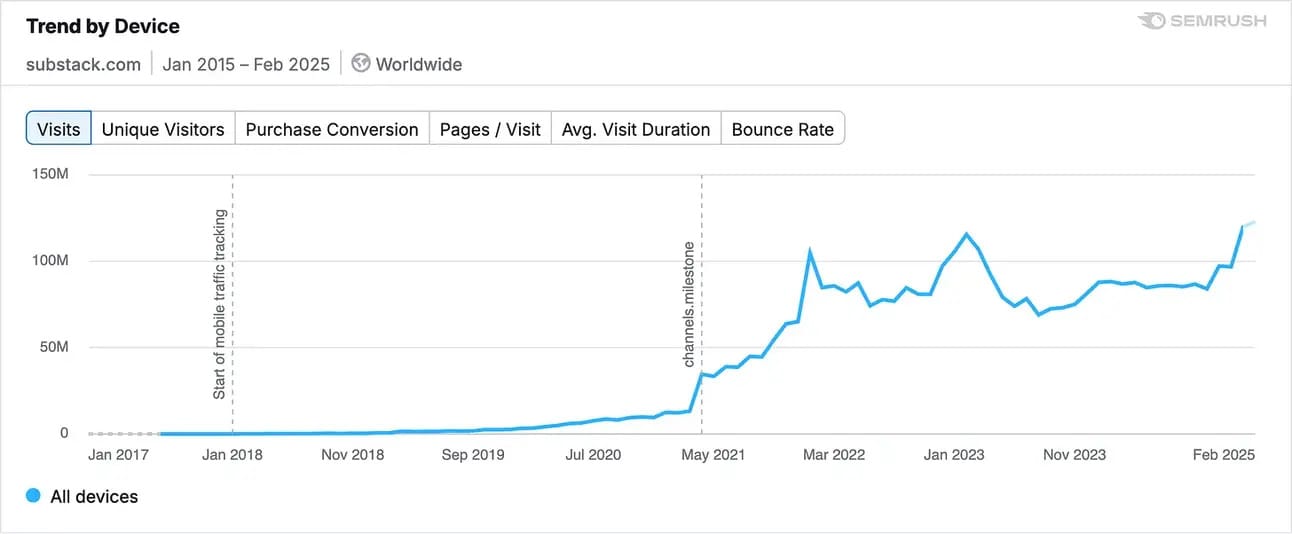
Long-form user opinions on Substack are attracting increasing numbers of users in the age of AI.
Robots
New burger bots create fast food to order in 27 seconds
Last week ABB Robotics and BurgerBots demonstrated a new fast food restaurant concept in tony Los Gatos, California, a suburb of San Francisco. As each order is received, a robot arm places a freshly-cooked burger onto a bun inside a burger box, which is then tagged with a QR code that details the toppings to be added. A conveyor belt then takes the burger-in-a-box past the topping stations, and the completed order is delivered ready for the customer 27 seconds after the order was made, untouched by human hands.

Robots will prepare your fast food order in 27 seconds.
Amazon develops a warehouse robot with a sense of touch
Online retail giant Amazon has announced that it has developed a new breed of warehouse robot, one that can “feel” as well as see. Amazon’s Vulcan robot has a mechanical arm that can sense the forces on its gripper, so it can deftly pick up and rearrange objects in a cart without damaging them. The arm is monitored by the robot’s AI-powered camera, to make sure that it picks the right items. Amazon says that Vulcan can handle approximately 75% of all items the company sells, and will alert a human when comes across an item that it can’t handle. It will be utilized at first only on the top and bottom shelves of the warehouse stacks, which are the hardest for humans to manage, because they require stooping or reaching. Amazon currently employs approximately 1,500,000 humans and 750,000 robots. That ratio is likely to shift progressively toward the robots.

Amazon’s Vulcan warehouse robot has a force-sensitive picking arm.
AI in Medicine
AI detects CHF in CT scans before patients have symptoms
Calcium-scoring CT scans identify and quantify calcified plaques in coronary arteries. Now scientists at Case Western Reserve University are developing AI models that analyze all the data in the calcium-scoring CT scans, and are finding that they can detect occult disease, such as incipient congestive heart failure, before the patient has any symptoms. AI’s ability to analyze images down to the pixel level, and to correlate multiple factors to discover subtle patterns, enable it to detect conditions far beyond the capability of the human eye. In the future, a single scan may be able to be analyzed to give a comprehensive view of the patient’s health in multiple organ systems.

AI can detect subtle patterns in CT scans which can predict cardiac risk.
Smart insoles can diagnose incipient dementia
Researchers from China and Ohio State University are developing solar-powered pressure-sensitive insoles that can detect patterns of pressure on the sole of the foot while walking, then transmit these patterns to a smartphone app. The data collected is analyzed by an AI model to detect abnormalities. Athletes can use the app to correct gait abnormalities that might reduce performance or even lead to injuries. Physicians can use the data to diagnose a variety of diseases, including of course joint and muscle diseases, but more surprisingly, to predict neuromuscular diseases like Parkinsonism, or even purely cognitive diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, which turns out to affect gait prior to some of the later cognitive deficits.

Soler powered, AI-enabled insoles are a surprising diagnostic tool of the future.
That's a wrap! More news next week.